Effect of Bread Improver Dough Conditioner used in Commercial Bread Production on Some Biochemical, Oxidative Stress and Haematological Parameters in Male Wistar Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
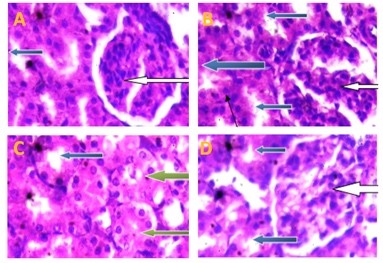
Bread improver dough conditioner (BIDC) is a blend of ingredients designed to enhance bread texture, volume, and taste. This study aimed to investigate the effect of BIDC used in bread production on human health, focusing on its potential impact on hematological, oxidative stress and biochemical markers in male Wistar rats. This study, which lasted 28 days, involved 20 male Wistar rats distributed in 4 groups, each group containing 5 animals. The first group was administered the normal diet, groups 2, 3 and 4 were administered three different doses consecutively 250 mg/kg, 1000 mg/kg and 2000 mg/kg of BIDC, and fed with a normal diet. In this study, results obtained revealed a significant decrease (p > 0.05) in body weight but no significant changes (p > 0.05) in liver and kidney weights of rats administered BIDC compared to the control. The rats administered 2000 mg/kg BIDC had a significant increase (p < 0.05) in serum superoxide dismutase levels and a decrease in catalase levels in comparison to the control. Biochemically, BIDC at 2000 mg/kg revealed no significant changes (p > 0.05) in alanine aminotransferase, cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, creatinine and urea levels, but decreased (p<0.05) triglycerides and aspartate aminotransferase levels, while increasing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels compared to the control. A significant increase (p>0.05) in platelet counts was recorded for 2000 mg/kg BIDC, but no significant changes (p>0.05) for white blood cells, red blood cells, hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Liver and kidney histopathology revealed no significant morphological damage across groups. In conclusion, BIDC exhibited no significant dose-dependent toxicity, except for final body weight and LDL-C levels suggesting that these substances are safe for consumption in low doses.
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Radhika K. The link between food, nutrition, diet and non-communicable diseases. Food and Nutrition. ACTA Sci. Nut. Health. 2014 DOI:10.31080/ASNH.2019.03.0422
Davidson PM, Sofos JN, Branen AL. Antimicrobials in food (3rd ed.). CRC Press. 2013
Saleh WA, Abdul Azeez BAM, Turki AA. Activity of quercetin derivatives as antibacterial, antioxidant and anticancer agents. Trop J Phytochem Pharm Sci. 2025, 4(8) 355 – 366 http://www.doi.org/10.26538/tjpps/v4i8.6
Imeson A. Food stabilisers, thickeners and gelling agents. Wiley-Blackwell. 2010
Downham A, Collins P. Colouring our foods in the last and next millennium. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2000; 35(1), 5–22. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2621.2000.00373.x
FAO/WHO. Evaluation of certain food additives: Seventy-fourth report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. WHO Tech. Rep. Ser. 966. 2011
Asioli, D, Aschemann-Witzel J, Caputo, V, Vecchio, R, Annunziata, A, Næs, T, Varela, P. Making sense of the “clean label” trends: A review of consumer food choice behavior and discussion of industry implications. Food Res. Int. 2017; 99, 58–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.022
Rosell CM, Rojas JA, Benedito BC. Influence of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality. Food Hydrocolloids. 2001; 15(1), 75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0268-005X(00)00054-0
World Health Organization Essential nutrition actions: Mainstreaming nutrition through the life course. https://www.who.int./publications/i/item/9789241515856. 2018
Nielsen, T.K, Kjolholt, J, Staplefeldt H. The use of redox agents in breadmaking. In S.P Cauvin, S.E. Salmon, L.S. Young (Eds.), Using cereal science and technology for the benefit of consumers. Woodhead Pub. 2005 (pp. 112-117).
Shahidi, F., & Zhong, Y. (2010). Revisiting the polar paradox theory: A critical overview. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010; 58(8), 2459–2470. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf903525w
Sivam AS, Sun-Waterhouse D, Quek SY, Perera CO. Properties of bread dough with added fiber polysaccharides and phenolic antioxidants: A review. J. Food Sci. 2010; 75(8), R163–R174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01844.x
Van der Maarel L, Van der Veen MJ, Uitdehaag B, Leemhuis JC, Dijkhuizen, HL. Properties and applications of starch-converting enzymes of the α-amylase family. J. Biotech. 2002; 94(2), 137–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(01)00407-2
Sluimer P. Principles of breadmaking: Functionality of raw materials and process steps. American Ass. Cereal Chem. (AACC). 2005.
Autio K, Laurikainen T. Relationships between flour/dough microstructure and dough handling and baking quality. Trends in Food Sci. Tech. 1997; 8(6), 181–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-2244(97)01045-3
Kurokawa Y, Maekawa A, Takahashi M, Hayashi Y. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of potassium bromate—A new renal carcinogen. Environ. Health Perspec. 1990; 87, 309–335. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9087309
Chassaing B, Koren O, Goodrich JK, Poole AC, Srinivasan S, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT. Dietary emulsifiers impact the mouse gut microbiota promoting colitis and metabolic syndrome. Nat. 2015; 519(7541), 92–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14232
World Health Organization Essential nutrition actions: Mainstreaming nutrition through the life course. https://www.who.int./publications/i/item/9789241515856. 2018
World Health Organization. Global report on the use of food additives in the processed food industry. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240057000. 2023
Kaushansky K, Lichtman MA, Prchl JT, Burns LJ, Caligiuri MA. Williams hematology. McGraw-Hill Education (9th ed.). 2016.
Bartels H, Böhmer M. Eine Mikromethode zur Kreatininbestimmung -A micromethod for the determination of creatinine. Clin. Chimica. Acta. 1972; 37(1), 193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(72)90432-9
Weatherburn MW. Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Analy. Chem. 1967; 39(8), 971–974. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60252a045
Smith JA, Chen T. Oxidative stress responses in wheat seedlings under drought conditions. J. Plant Phys. 2022, 275, 153753.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2022.153753
Saiprasanna AP, Sahoo PK, Mahapatra RK. A histopathology study caninw cutaneous neoplasms. Indian J. Vet. Path. 2017; 41(3), 202-207
Bartels H, Böhmer M. Eine Mikromethode zur Kreatininbestimmung -A micromethod for the determination of creatinine. Clin. Chimica. Acta. 1972; 37(1), 193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(72)90432-9
Ugwah-Oguejiofor CJ, Okoli CO, Ugwah MO, Umaru ML. Acute and sub-acute toxicity of aqueous extract of aerial parts of Caralluma dalzielii N. E. Brown in mice and rats. Heliyon. 2019; 5(8), e02280.
OECD. Test No. 408: Repeated dose 90-day oral toxicity study in rodents. OECD Publishing. 2018, https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264070707-en
Maekawa A, Onodera H, Furuta K, Matsuoka C, Ohho, Y, Odoshima, S. Carcinogenicity studies of sodium nitrite and sodium nitrate in F-344 rats. Fd. Chem. Toxic. 1982: 20: 25-33.
Til HP, Falke HE, Prinsen MK, Willams MI. Acute and subacute toxicity of tyramine, spermidine, spermine, putrescine and cadaverine in rats. Food Chem. Tox. 1997; 35(3-4), 337–348.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-6915(97)00021-6
Abdelaziz AM, El-Zahab HS, Ghonim SI. Effects of some synthetic food colouring on the thyroid functions and lipidperoxide in rats. Egypt. J. Hospital Med. 1997; 6(1), 92–107.
Borzelleca JF, Hogan GK. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity study of FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) in rats. J. Tox. 1989; 8(3), 185–196. https://doi.org/10.3109/15569528909048770
Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis. Nat. 2000, 407(6801), 233–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/35025203
Libby P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nat. 2021, 592(7855), 524–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03392-8
Borén J, Chapman MJ, Krauss RM, Packard CJ, Bentzon JF, Binder CJ, Daemen MJ, Demer LL, Hegele RA, Nicholls SJ, Nordestgaard BG, Watts GF, Bruckert E, Fazio S, Ference BA, Graham ., Horton JD, Landmesser U, Laufs U, Taskinen MR. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Euro. Heart J. 2020, 41(24), 2313–2330. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz962
Falk E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J. Amer Coll. Cardio. 2016, 47(8 Suppl), C7-C12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2005.09.068
Wang W, Srivastava S. Serological markers. In Breslow, Lester. Encyclopedia of Public Health. New York. Macmillan, USA. 2002; pp. 1088-1090, 2002.
Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. (Eds.). Sleisenger and Fordtran’s gastrointestinal and liver disease: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, management (11th ed.). Elsevier. 2021
Levy AS, Bosch JP, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate way to determine glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: A new prediction equation. Ann. Intern. Med.,130 (6, 461-470.)
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM. Free radicals in biology and medicine (5th ed.). Oxford University Press. 2015.
Kessler A, You Y, Hati S, Li Y. Tert-butylhydroquinone: A double-edged sword in food safety and its role in health. Food Chem. Tox. 2022, 159, 112757.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112757
Wolff MS, Britton AP, Wallace KB. Toxicol. Rep., 6, 121-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.01.003
Femi-oloye TT, Afolabi OK, Fafure AA. Dose-dependent toxic effects of sodium benzoate on the histology of the stomach, liver, kidney and brain and on the haematological parameters in Wistar rats. Tox. Res. App. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1177/2397847320929816
Kaser A, Brandacher G, Steurer W, Offner FA. Interleukin-6 stimulates thrombopoiesis through thrombopoietin: Role in inflammatory thrombocytosis. Blood. 2001, 98(9), 2720-2725
Kaushansky K, Lichtman MA, Prchl JT, Burns LJ, Caligiuri MA. Williams hematology. McGraw-Hill Education (9th ed.). 2016.
Ebhohon, SO, Asoya, EV, Iyare, HE, Akerele, OR, Ezedimbu, MC (2023). Effect of Aqueous Leaf Extract of Justicia carnea on Hematological Parameters of Male Wistar Rats Exposed to Thioacetamide. Trop. J. Phytochem. Pharm. Sci., 2(2), 55–58.
Sasaki K, Yamaguchi T, Tanka Y. Histopathology of kidney and liver diseases. J. Clin. Path. 2019, 72(8), 505-510. https://doi/10.1136/jclinpath-2019-205912.
Janette, W. M., Roberts, G. K., & Albassam, M. A. (2013). Histopathological assessment of drug-induced liver and kidney injury in preclinical safety studies. Toxicol. Pathol., 41(5), 770-784. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623312467520