Effect of Lacatomtom Drink on Spatial Memory in Male Wistar Rat
Main Article Content
Abstract
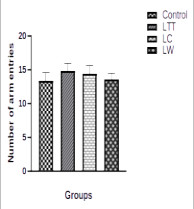
Lacatomtom is one of the emerging psychoactive substances abused by youths in Nigeria. It’s a mixture of tomtom candy and lacasera drink. The abuse of this substance has led to some pyschosocial deficit, this deficit are thought to be as a result of memory impairment. This study is therefore designed to look at the effect of lacatomtom on spatial memory in male Wistar rats. Twenty (20) Wistar rats weighing 120-150 g were randomly divided, five (5) each in a group of four (4). Group A served as control and received 1 mL/kg distilled water orally. Group B received 1 mL/kg of Lacatomtom (LTT) orally, meanwhile group C took 1 mL/kg Lacasera ( LC) orally. Group D received 1 mL/kg Lacawater (LW) orally. Animals were treated once, five minutes later, they were allowed to undergo the Y -maze test. Percentage alternations and number of entry was calculated for each group. Data were analysed using ANOVA at α 0.05. There was no significant difference in the arm entry in all the groups. Although the LTT group has the highest mean entry (14.8 ± 1.16) followed by the LC group (14.4 ± 1.21) and LW group (13.6 ± 0.93). The lowest entry observed was the control group (13.4 ± 1.21). There was a significant difference in the percentage alternation in the LTT group when compared to the control group.
The findings from this study suggests that Lacatomtom alters the spatial memory function of the brain in Wistar rats through mechanisms that may be dependent on the activation of opoidergic system in the brain.
Metrics
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
References
Docherty J. R. Pharmacology of stimulants prohibited by the world anti-doping agency (WADA). Br J Pharmacol. 2008; 154(3): 606-622.
Ijediogor G, Ezea S, Awodipe T, Diamond M, Ekemezie H. Drug addiction among the youth: a ticking time bomb. The Guardian. 2018. Available from: https://guardian.ng/saturday-magazine/drug-addictionamong-the-youth-a-ticking-time-bomb.
Mustapha AK. Codeine: addicts now use Lacasera and Tomtom to form “gigabyte” solution-NDLEA. Peoples Daily Newspaper. 2018. Available from: https://peoplesdailyng.com/codeine-addicts-now-uselacasera-tomtom-to-form-gigabyte-solution-ndlea.
Pennings EJM, Leccese AP, Wolff FA de. Effects of concurrent use of alcohol and cocaine. Addiction. 2002; 97(7):773–783.
Miller SC, Fiellin DA, Rosenthal RN, Saitz R. American Society of Addiction Medicine. The Asam Principles of Addiction Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2019.
Olson-Madden JH, Brenner LA, Corrigan JD, Emrick CD, Britton PC. Substance use and mild traumatic brain injury risk reduction and prevention: a novel model for treatment. Rehab. Res. Prac. 2012, 174579.
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Mind Matters: Drugs and the Brain. 2019
Hughes RN. The value of spontaneous alternation behavior (SAB) as a test of retention in pharmacological investigations of memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev.. 2004; 28(5):497–505.
Momeni S, Segerström L, Roman E. Supplier-dependent differences in intermittent voluntary alcohol intake and response to naltrexone in Wistar rats. J. Front. Neurosci. 2015; 9(424).
Tingxu Yan, Bosai He, Shutong Wan, Mengjie Xu, Huilin Yang, Feng Xiao, Kaishun Bi, Ying Jia. Antidepressant-like effects and cognitive enhancement of Schisandra chinensis in chronic unpredictable mild stress mice and its related mechanism. Scientific Reports. 2017; 7(1):6903.
Tursun Alkam, Toshitaka Nabeshima, Chapter 4 - Modeling the Positive Symptoms of Schizophreni. In: Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience. Edited by: Mikhail V. Pletnikov, John L. Waddington, Elsevier. Volume 23, 2016 ,Pages 39-54.
Abdel-Ghany R, Nabil M, Abdel-Aal M, Barakat W. Nalbuphine could decrease the rewarding effect induced by tramadol in mice while enhancing its antinociceptive activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015; 758:11–15.
Flood JF, Cherkin A, Morley JE. Antagonism of endogenous opioids modulates memory processing. Brain Res. 1987; 422:218–234.
Hosseini-Sharifabad A, Rabbani M, Sharifzadeh M, Bagheri N. Acute and chronic tramadol administration impairs spatial memory in rats. Res Pharm Sci. 2016 ;11(1):49-57. PMID: 27051432; PMCID: PMC4794937.
Lekana C, Miguel LM, Dobhat-Doukakini CR, Abena AA. Effects of tramadol on exploratory behaviour,anxiety and memory in BALB/C mice: 49-day oral dosing study. Scholarly J Sci Res Essay.2024; 6 (6): 1-9.
Benjamin Essien. A comparative analytical study of airborne pollen grains, spores and other palynomorphs within Grimard Catholic Hospital, Anyigba, Kogi state, Nigeria. Scholarly J Sci Res Essay. 2014; 3(5):56-60